All About Supply Chain
May 17, 2024 By Susan Kelly
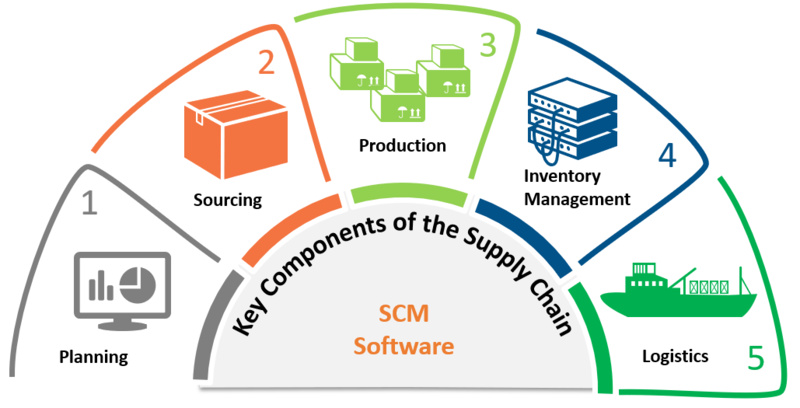
To understand supply chain management, it is necessary to know the parts of a supply chain. A supply chain includes all steps required to take a product from where it was made to the final consumer. This begins with acquiring raw materials and progresses through production before concluding in product distribution.
Procurement and Sourcing
Procurement is like a cornerstone in supply chain management. It manages the process of getting raw materials or parts that are needed for making products. This includes planning, bargaining, and working together with suppliers to make sure resources are available at the right time. Sourcing, which is an important part of procurement, looks more deeply into selecting a supplier according to certain criteria such as where they're located geographically, their ability to produce, and the ethical methods they follow. Effective sourcing strategies are not just about reducing costs but also emphasizing getting good quality and dependable supplies. They help in building strong relationships with suppliers.
Aside from the usual ways of getting goods, many companies are starting to adopt sustainable sourcing. This thinking about sustainability goes past just environmental effects and includes aspects related to society and ethics like fair work ways or involvement in community matters. Companies that give importance to sustainable sourcing can lessen risks linked with supply chain interruptions, boost brand status, and help towards worldwide sustainability aims.
- Risk Mitigation: Procurement strategies should include risk assessment and mitigation plans to address potential supply chain disruptions, such as natural disasters or geopolitical events.
- Supplier Diversity: Embracing supplier diversity initiatives can foster innovation, promote economic growth in underrepresented communities, and mitigate risks associated with dependence on a single supplier.
Manufacturing and Production
Manufacturing and production processes are the foundation of the supply chain. They change raw materials into final products that can be distributed. Having operations that work smoothly and productive methods of production is very important to meet what consumers want while keeping expenses low. Lean manufacturing rules, which include just-in-time inventory and ongoing enhancement, help in making production workflows better, reducing waste, and improving productivity.
In the worldwide business setting of today, manufacturing activities are using digital tools such as 3D printing and robots more and more to improve their efficiency and adaptability. Modern methods for making things help in maintaining flexible production processes that can be customized or quickly adjusted according to market needs. Also, automation within the field of manufacturing works not just towards enhancing how well operations function but also makes products better in terms of quality and consistency which leads to increased customer contentment.
- Quality Control: Implementing robust quality control measures throughout the production process ensures adherence to product specifications, minimizes defects, and enhances customer satisfaction.
- Supply Chain Resilience: Manufacturing operations should prioritize resilience by diversifying suppliers, establishing redundant production capabilities, and investing in contingency planning to mitigate risks posed by disruptions.
Inventory Management
Managing inventory is a very important part of optimizing supply chains, making sure that there are enough products at the correct time to meet customer requests. To stop stockouts or too much stock, it's crucial to predict the demand precisely which could cause higher carrying costs and possible obsolescence. Getting an ideal stocking level means you find a balance between variations in demands, times taken to deliver and how much service is needed.
Also, recent methods of managing inventory use data analysis and forecasting models to improve decision-making and inventory adjustments. With help from studying past sales information along with market tendencies plus seasonal patterns, businesses can make better predictions about future demand. This leads to optimizing how they refill their stockroom supplies or goods available for sale. Furthermore, measures for controlling stock like ABC analysis and the "just-in-time" system assist in prioritizing resources effectively while also minimizing holding expenses.
- Supplier Collaboration: Collaborating closely with suppliers and sharing demand forecasts can improve inventory visibility upstream in the supply chain, enabling proactive inventory management and reducing lead times.
- Economic Order Quantity (EOQ): Calculating the EOQ helps determine the optimal order quantity that minimizes total inventory costs, considering factors such as ordering costs, holding costs, and demand variability.
Logistics and Transportation
Logistics includes the detailed arranging, doing, and controlling of moving goods as well as their storage in a supply chain. Logistics needs to work efficiently because it can help make transport routes, warehouse use, and order completion methods better. This makes sure that things are delivered on time and distributed at a low cost. Logistics also involves managing different kinds of transportation like trucks, ships, trains, and planes among others. The aim is to match customer requirements while keeping a check on transport expenses and transit durations.
In addition, the increase in e-commerce has encouraged new methods for final delivery like drones and self-driving vehicles. These are made to improve how fast and easy it is to deliver products. Tracking tools that show real-time movement let everyone involved see the whole supply chain. This helps them monitor the progress of shipments and take quick action if there are any issues or delays.
- Reverse Logistics: Managing reverse logistics processes, including returns and product recalls, is crucial for maintaining customer satisfaction and optimizing resource recovery and disposal.
- Transportation Optimization: Leveraging route optimization software and load consolidation strategies can minimize fuel consumption, reduce carbon emissions, and lower transportation costs.
Distribution and Fulfillment
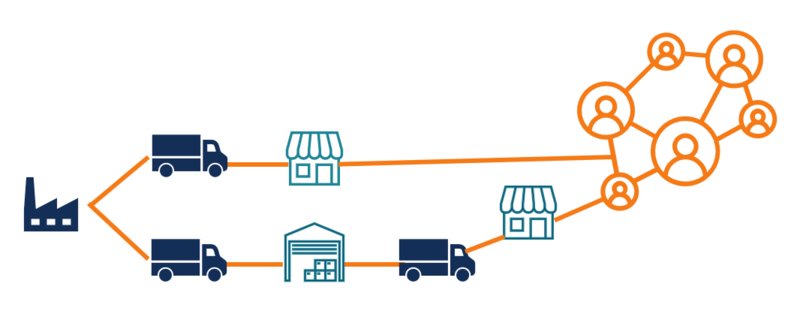
Distribution is the end part of the supply chain journey. Here, products are given to customers or put in retail places such as shops. Fulfillment centers have a very important job in keeping products and sending them out correctly to meet customer needs for fast delivery and order precision. Planning where to put warehouses and making their layout better are important methods that help with being close to main markets and making order fulfillment processes easier.
Also, a multi-channel distribution plan can allow companies to communicate with their customers through various selling routes such as physical stores, online trading platforms, and mobile apps. This method gives the advantage of smoothly joining different channels for businesses. They can improve how customers experience their services or products and also boost chances of making sales while building up devotion towards the brand name.
- Order Accuracy: Implementing robust quality control measures in fulfillment processes minimizes order errors, reduces returns, and enhances customer satisfaction.
- Inventory Visibility: Utilizing advanced inventory management systems and RFID technology provides real-time visibility into inventory levels across distribution channels, enabling better demand forecasting and inventory replenishment decisions.
Technology in SCM
Technology has changed supply chain management by giving businesses abilities to improve efficiency, visibility, and decision-making. Automation technologies like robotics, or autonomous guided vehicles (AGVs), can help in making repetitive tasks easier in warehouses and factories. This lowers costs for labor while increasing operational effectiveness. When companies automate routine processes, they free up human resources for more strategic roles which encourages innovation and boosts competitive edge.
Additionally, data analytics is very important for getting the most out of supply chains. It helps businesses to use their large amount of data from different parts of the chain and turn it into useful actions. For example, predictive analytics algorithms predict demand and can find trends or possible disruptions - this helps businesses be ready beforehand for problems and take advantage when chances arise. Also, artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning algorithms improve planning handling in supply chains which promotes ongoing enhancement along with adaptability towards changing market situations.
- Cybersecurity: Protecting supply chain data and systems from cyber threats is paramount to safeguarding sensitive information, maintaining operational continuity, and preserving customer trust.
- Interconnectivity: Leveraging Internet of Things (IoT) devices and sensor technology enables real-time monitoring of supply chain assets, enhancing visibility, and enabling proactive decision-making to optimize operational performance.
Conclusion
Supply chain management is a complicated but necessary part of current business activities. When we learn about its details- from buying materials to giving out finished products- companies can make their processes work at the top level, keep costs low, and give good service to customers. Using technology and following the best ways are very important for doing well in today's market where competition is high.








